Data management
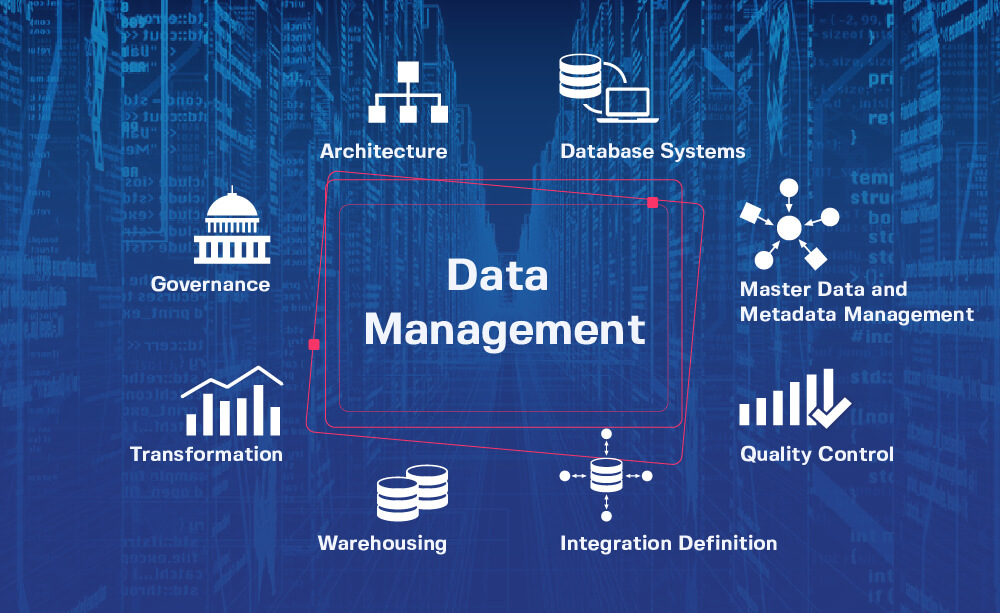
Data management is the process of ingesting, storing, organizing and maintaining the data created and collected by an organization. Effective data management is a crucial piece of deploying the IT systems that run business applications and provide analytical information to help drive operational decision-making and strategic planning by corporate executives, business managers and other end users.
Importance of data management
Data increasingly is seen as a corporate asset that can be used to make more-informed business decisions, improve marketing campaigns, optimize business operations and reduce costs, all with the goal of increasing revenue and profits. But a lack of proper data management can saddle organizations with incompatible data silos, inconsistent data sets and data quality problems that limit their ability to run business intelligence (BI) and analytics applications — or, worse, lead to faulty findings.
Data management has also grown in importance as businesses are subjected to an increasing number of regulatory compliance requirements, including data privacy and protection laws such as GDPR and the California Consumer Privacy Act. In addition, companies are capturing ever-larger volumes of data and a wider variety of data types, both hallmarks of the big data systems many have deployed. Without good data management, such environments can become unwieldy and hard to navigate.


Types of data management functions
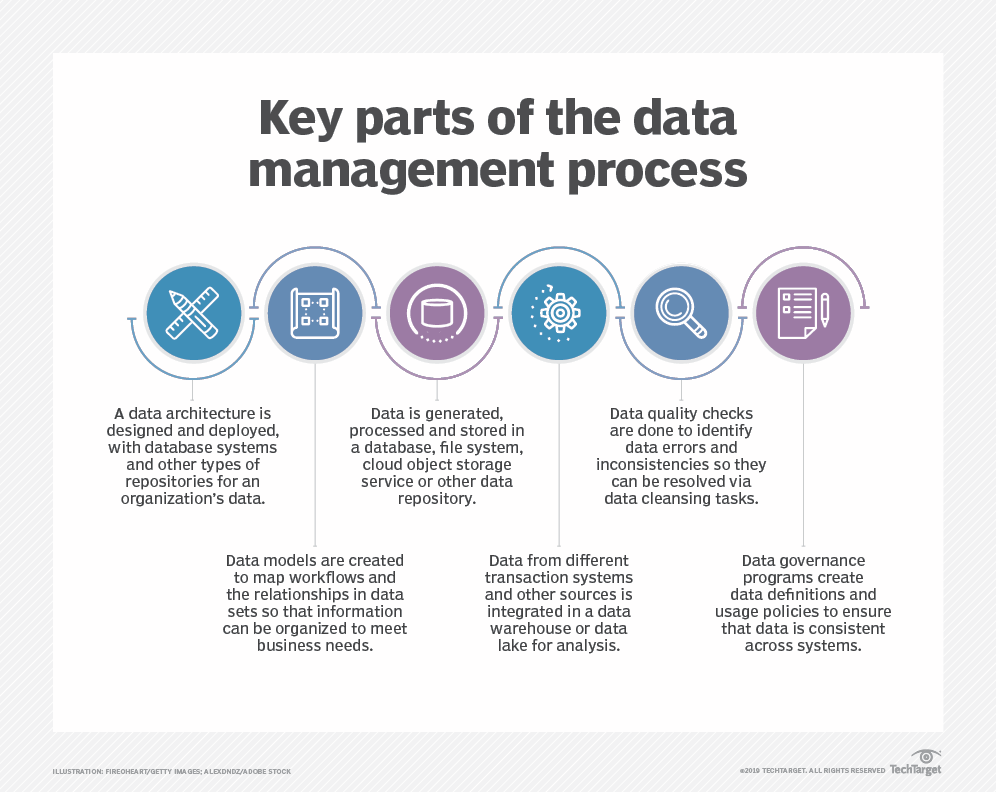
The separate disciplines that are part of the overall data management process cover a series of steps, from data processing and storage to governance of how data is formatted and used in operational and analytical systems. Development of a data architecture is often the first step, particularly in large organizations with lots of data to manage. An architecture provides a blueprint for the databases and other data platforms that will be deployed, including specific technologies to fit individual applications.
Databases are the most common platform used to hold corporate data; they contain a collection of data that’s organized so it can be accessed, updated and managed. They’re used in both transaction processing systems that create operational data, such as customer records and sales orders, and data warehouses, which store consolidated data sets from business systems for BI and analytics.
Database administration is a core data management function. Once databases have been set up, performance monitoring and tuning must be done to maintain acceptable response times on database queries that users run to get information from the data stored in them. Other administrative tasks include database design, configuration, installation and updates; data security; database backup and recovery; and application of software upgrades and security patches.